The human hairline, a subtle yet defining feature, comes in a myriad of shapes and forms. Among these, one distinct pattern often sparks curiosity and sometimes, misconception: the V hairline. More commonly known as a "widow’s peak," this particular hairline configuration is a fascinating example of genetic diversity, often misunderstood as a sign of impending hair loss rather than a natural, inherited trait. This comprehensive article delves into what exactly a V hairline is, its genetic underpinnings, its variations, and crucially, how it differs from a receding hairline, offering clarity and insight into this unique characteristic.
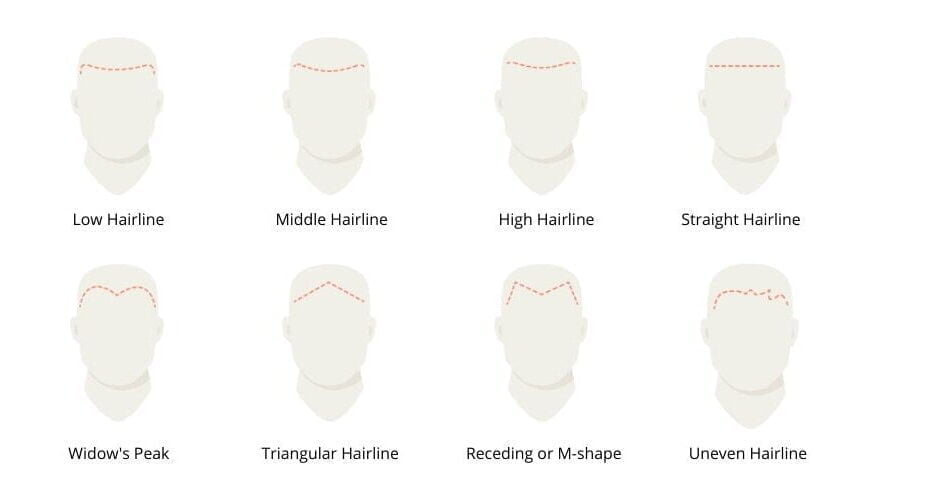
What Exactly is a V Hairline?
At its core, a V hairline is characterized by a distinctive V-shaped point of hair that descends towards the center of the forehead, forming a triangular or pointed shape. Instead of a straight or gently curved line across the forehead, the hair growth extends further down in the middle, creating a visible "peak." This central point can vary in prominence, from a subtle dip to a sharply defined, pronounced triangle. The term "widow’s peak" itself carries a touch of historical folklore, believed to originate from the pointed caps worn by widows in the 16th century, or perhaps from the superstitious belief that such a hairline foreshadowed early widowhood. Despite these historical associations, a V hairline is simply a natural variation in the pattern of hair growth.
Unlike a straight hairline where the hair forms a relatively even line across the forehead, or a receding hairline where the hair pulls back, particularly at the temples, a V hairline is a stable feature. It is present from birth or becomes apparent during early development and typically remains consistent throughout an individual’s life, unless influenced by external factors like significant hair loss or trauma.
The Genetics Behind the V Hairline
The primary determinant of whether an individual possesses a V hairline is genetics. It is widely considered an inherited trait, passed down through families. While the exact genetic mechanism is complex and not fully understood, it is often described as an autosomal dominant trait. This means that if you inherit just one copy of the gene responsible for a V hairline from either parent, you are likely to express the trait. However, like many genetic traits, its expression can vary, meaning some individuals might have a very prominent peak, while others have a more subtle one, even within the same family.
The development of a V hairline is rooted in the embryonic stage, specifically during the formation of the facial structures and hair follicles. The arrangement and migration of cells that will eventually form the hair follicles on the scalp and forehead are genetically predetermined. In individuals with a V hairline, there’s a specific pattern of cell migration that results in the central point of hair growth extending further down the forehead than the hair at the temples. This genetic blueprint dictates the shape of the hairline, making it a fundamental part of an individual’s natural appearance rather than an acquired condition.
It’s important to note that while the presence of a V hairline is genetic, its exact appearance can be influenced by other genetic factors or even the overall density and texture of a person’s hair. This explains why not all V hairlines look identical, even among family members who share the trait.
Variations and Spectrum of V Hairlines
Just as no two individuals are exactly alike, neither are all V hairlines. There’s a wide spectrum of appearances, ranging from barely noticeable to strikingly prominent. Understanding these variations helps in appreciating the diversity of this genetic trait:
- Sharp vs. Subtle Peaks: Some individuals exhibit a very sharp, distinct point that clearly descends into the forehead. Others may have a more rounded or subtle V, where the central point is less pronounced and blends more gently into the surrounding hairline.
- High vs. Low Peaks: The peak can originate higher up on the forehead, making the overall hairline appear higher, or it can start lower, creating a shorter forehead appearance.
- Symmetrical vs. Slightly Asymmetrical: While typically symmetrical, some V hairlines might have a slight asymmetry, with one side of the "V" being marginally longer or more pronounced than the other. This is usually a minor variation and not a cause for concern.
- Hair Density: The density of the hair within the V can also vary. Some individuals might have very thick, dense hair forming the peak, while others have finer or sparser hair in that area, which can make the peak less obvious.
These variations are all considered normal and are part of the natural diversity of human hairlines. The appearance of a V hairline can also be influenced by hair styling; for instance, pulling hair back tightly can emphasize the peak, while bangs or a fringe can effectively conceal it.
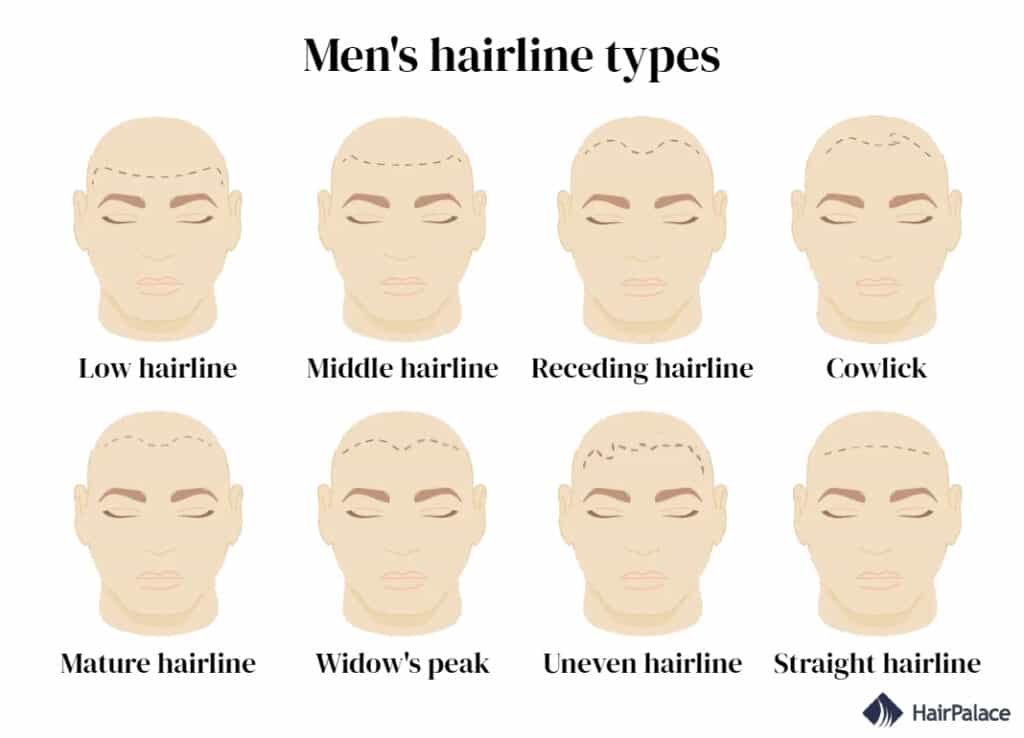
V Hairline vs. Receding Hairline: A Crucial Distinction
One of the most common sources of confusion and anxiety surrounding the V hairline is its potential misidentification with a receding hairline, particularly in men. While both involve the hairline, their underlying causes and implications are fundamentally different.
-
V Hairline (Widow’s Peak):
- Nature: A stable, genetically determined pattern of hair growth.
- Origin: Present from birth or early childhood.
- Progression: Does not typically change or "recede" on its own over time. The central point remains consistent.
- Appearance: Characterized by a central V-shaped point. The hair density around the peak and at the temples remains full.
-
Receding Hairline (Androgenetic Alopecia/Male Pattern Baldness):
- Nature: A progressive form of hair loss, primarily caused by genetics and hormones (dihydrotestosterone or DHT).
- Origin: Typically begins in adulthood, often in the late teens or early twenties, and progresses with age.
- Progression: Characterized by a gradual retreat of the hairline, usually starting at the temples and sometimes forming an "M" shape. The central part of the hairline might initially remain, creating a pseudo-V shape as the sides recede, but eventually, the entire hairline can move backward.
- Appearance: Involves thinning and loss of hair density, particularly at the temples and frontal scalp. The skin becomes more visible, and the hairline appears to move further back on the head.
How to Tell the Difference:
- History: Have you always had this V-shape, or is it a recent development? If it’s always been there, it’s likely a natural V hairline.
- Progression: Is the V-shape stable, or is the hair around it, especially at the temples, becoming thinner or moving further back? If the latter, it points towards recession.
- Hair Density: Is the hair within the V and at the temples as dense as the rest of your hair, or is it noticeably thinner? Thinning is a hallmark of hair loss.
- Family History: While a V hairline is genetic, so is androgenetic alopecia. Look at older male relatives for patterns of hair loss.
If there’s uncertainty or concern about hair loss, consulting a dermatologist or a trichologist (hair and scalp specialist) is advisable. They can accurately diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate steps if hair loss is indeed occurring.
Cultural Perceptions and Historical Significance
Beyond its biological definition, the V hairline has held various cultural and symbolic meanings throughout history. As mentioned, the term "widow’s peak" itself evokes a sense of historical mystique. In some folklore, it was associated with misfortune or an early death, particularly for women. However, these are merely superstitions and have no basis in reality.
In modern culture, the perception of a V hairline has largely shifted. It is often seen as a distinctive and attractive feature, gracing the foreheads of numerous celebrities and public figures. It can add character and uniqueness to a person’s appearance, often contributing to a striking or elegant look. Rather than being a flaw, it’s now widely accepted and even celebrated as a unique aspect of one’s natural beauty.
Living with a V Hairline: Styling and Care
For individuals with a V hairline, no special care is typically required for the hairline itself. General hair care practices—washing, conditioning, and maintaining a healthy diet—are sufficient to keep the hair and scalp in good condition.
When it comes to styling, a V hairline offers several versatile options:
- Embracing It: Many people choose to highlight their V hairline. Styles that pull the hair back, such as ponytails, buns, or slicked-back looks, can beautifully showcase the peak. A center part can also draw attention to the symmetry of the V.
- Minimizing It: If an individual prefers to soften or conceal their V hairline, certain hairstyles can achieve this. Bangs (fringes) are an excellent option, as they fall over the forehead and effectively hide the peak. Side parts can also help by drawing hair across the forehead, breaking up the central point. Layered cuts around the face can also help blend the hairline.
- Haircuts: Specific haircuts can complement a V hairline. For men, styles that have some length on top but are shorter on the sides can work well. For women, layered cuts or styles with face-framing pieces can enhance or soften the hairline as desired.
The key is to choose a style that makes you feel confident and comfortable, whether you choose to emphasize or downplay your V hairline.
When to Be Concerned: Potential Issues
While a V hairline is a normal genetic trait, there are instances when its appearance might warrant attention from a medical professional:
- Sudden Changes: If a previously stable V hairline begins to noticeably recede, thin, or change its shape rapidly, it could be a sign of underlying hair loss conditions like androgenetic alopecia or telogen effluvium.
- Accompanying Symptoms: If the V hairline’s change is accompanied by other symptoms such as scalp itching, redness, pain, or significant overall hair shedding, it’s important to seek medical advice.
- Asymmetry: While slight asymmetry is normal, a sudden or pronounced asymmetry in the hairline that wasn’t previously present could indicate a problem.
In such cases, a dermatologist or trichologist can perform a thorough examination, diagnose the cause of any changes, and recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.
Conclusion
The V hairline, or widow’s peak, is a fascinating and common genetic trait that adds to the rich tapestry of human diversity. Far from being a flaw or a precursor to baldness, it is a natural and often distinctive feature that has graced individuals throughout history. Understanding its genetic origins, recognizing its various forms, and critically distinguishing it from a receding hairline are crucial for dispelling misconceptions and fostering self-acceptance. Whether embraced or subtly styled, a V hairline is simply another beautiful variation in the human form, a testament to the intricate and diverse ways our genes express themselves.
![]()